Node Programming
Node or Flow-based programming is a way to create simple expressions and logic by connecting individual instructions (called nodes) together in what is called a node graph.
The name 'flow' programming comes from the fact that values travel between the nodes through connections that can be thought of as if they were pipes - carrying data from the input nodes to the output nodes.
It's the backbone of the Visual Analytics System.
Nodes
A single node can have…
| Attribute | Usage |
|---|---|
| Type | Describes what job they perform. |
| Options | Options that adjust what the node does. |
| Inputs | Used to bring data in from other nodes. |
| Outputs | Send the results to other nodes. |
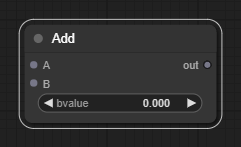
For example, above is the Add node - it has two inputs (left), which are the numbers it will add together, a single option named bvalue and an output (right) of the result.
Connections
Below is a simple example of a calculation graph, designed to add two numbers together - we'll add the numbers '8' and '5'.
We begin with two Number nodes. The node has no inputs, but has an option - the value we want to send through the output.
Next, we have an Add node. As we saw before, it has two inputs - the two numbers we want to add together.
We pipe the outputs of our number nodes into the inputs of our add node - the numbers 8 and 5 flow in.
The add node sends the total of the two numbers out the other side, which is fed into an Calculation Output node, which delivers the final number to be analysed.
Strengths
Node programming is one of the easiest visual programming methods, allowing people to explain simple logic and math without resorting to code or text.
Weaknesses
The primary weakness of node-based-programming is that it doesn't deal well with complexity. It's suited to fairly simple logic - once you need several different levels of logic and large sets of 'IFs', 'ANDs' and 'ORs', you might be better off creating a solution with Python.