Optimisation
Optimisation is designed to help you find the ideal combination of attributes (that you are Capturing) to achieve a specific target outcome.
For example, you might have a Capture that records your cupcake manufacturing line and has the oven temperature, fan speed, conveyor speed from the ovens, and the internal cake temperature from the inspection area.
This system could then be used to try and calculate the ideal oven temp, fan speed and line speed to achieve the perfect temperature.
Optimising
First, filter the list for the type of product you're hoping to make.
Then press the Optimise button in the capture list - this will allow you to perform an optimisation.
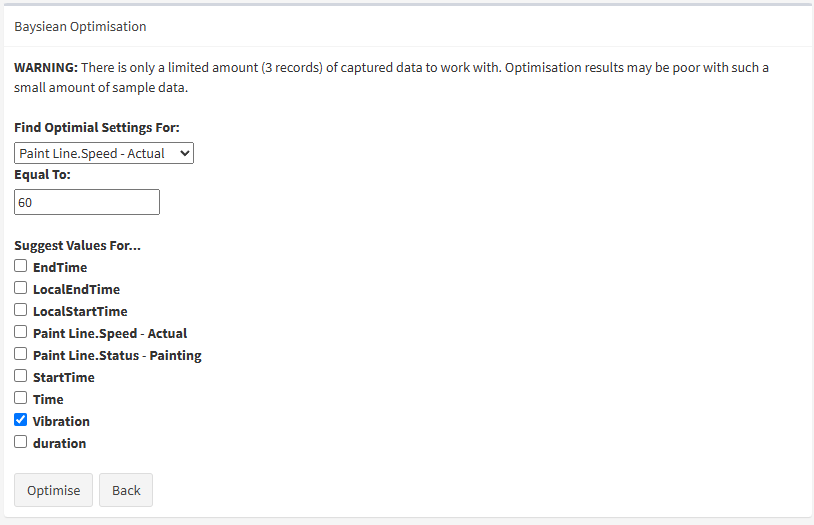
You'll need to choose the following…
1) The attribute you're trying to optimise (ie. Internal Cake Temp).
2) The value you're trying to achieve (ie. 98 Deg C).
3) The inputs you want to set (ie. Line Speed, Oven Temp, Fan Speed).
Then press Optimise to continue.
Results
After a few moments, the results will appear.
There will be a list of all of the inputs you chose (ie. Line Speed, Oven Temp etc.), followed by the suggested values.
These can be used to guide tests and experiments, refine control or estimate values.
NOTE: If results from Bayesian Optimisation aren't very useful, you may want to consider using Machine Learning. It's more capable of working with complex, interconnected systems.
Usage Notes
It's important to remember that the 'input' and 'output' of your optimisation don't have to be the inputs and outputs of your process.
If you have both vibration and machine speed, you can use optimisation to both…
* Estimate the vibration based on speed, or vice-versa,
* Estimate the speed based on vibration.