Coordinate Mapping
ARDI stores the position of your assets based on an arbitrary coordinate system that is created when you first build your environment.
For example, you may have created an empty environment that is 200×200 units long and wide, or based your environment off a photograph that was 1200×1900 pixels across.
But these values don't translate into anything real world - often the drawings or images you base your environment on aren't aligned with north, and 1 unit of ARDI distance could be a millimetre or a kilometre - there's no obvious way of converting ARDI positions to real-world ones.
Coordinate mapping gives ARDI the infromation it needs to convert its own internal positional data to real-world measurements.
ARDI currently supports two different non-ARDI coordinate systems - Real World and GPS.
Real World Coordinates
Real World coordinates are usually measured in meters east and meters north and work very much like a pirate map. You choose one point in your environment as the 'start point' and give it a value of '0,0', then every other location is measured in units east and units north of that point.
Note that units above are you choice of real-world measurement unit, but it ideally should be in metres. However, US users may choose to use yards or feet instead.
Configuring this type of measurement mapping allows you to calculate real-world distances between objects in your ARDI system.
GPS
GPS coordinates are very straight-forward - they are the position in degrees latitude and degrees longitude.
Configuring GPS mapping allows you to place objects in your scene based on GPS location data - either from maps, or for dynamically-positioned equipment.
Configuring
There are a few steps to configuring your 'mapping' between the three different coordinate systems.
As well as your existing web session, we suggest..
a) Opening the ARDI map of the location, and
b) Opening a Google Maps map of the location.
The Process
1) Go to your environment asset and choose Placement & 3D | Update 3D Environment and choose Coordinate Mapping
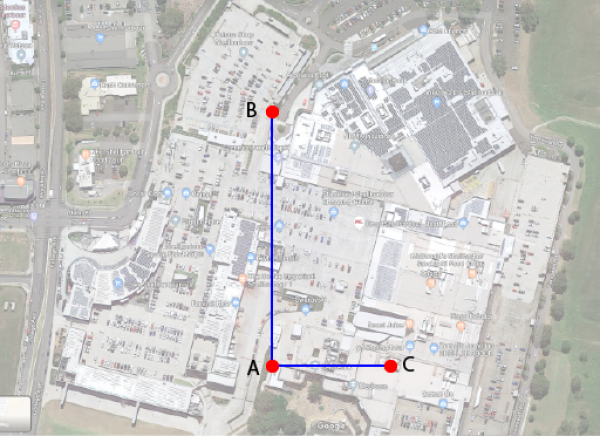
2) Choose three points on your ARDI map that form an 'L' shape. See points A, B & C in the diagram below. We suggest choosing points that you can easily spot in both the map and your satellite imagery.
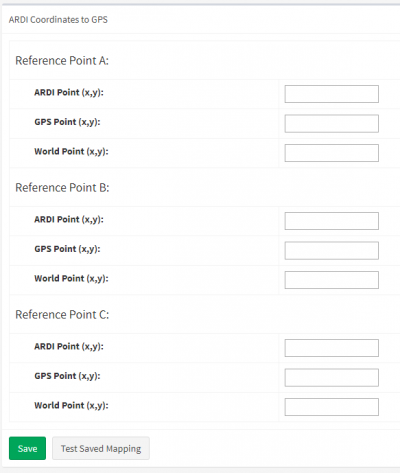
3) Enter the details of the three points in ARDI coordinates. You can find these in the top-right of the map web page when you hover your mouse over them.
4) Enter the details of the three points in GPS coordinates from the Google maps. You can find these by left-clicking on the point - the exact GPS location will appear at the bottom of the page.
5) Enter the details of three points in East/North coordinates. The easiest way to do this is to right clicking in Google Maps choosing Measure Distance. Left-clicking will then allow you to measure the distance along each of these lines horizontally and vertically, then enter those details in.
GPS Accuracy Note: Because GPS coordinates are not linear, ARDI may lose precision when converting GPS coordinates in very large (+2km) environments. However for anything smaller than this, the accuracy losses are minimal.
Once all of these figures are in, you can save them. ARDI will then be able to freely convert between each of these three coordinate systems.